Argentina
Argentina is a place where nature and human development seek balance. Natural systems drive sustainable economies, offering people opportunities to improve livelihoods for the decades to come.

Diversity of natural resources, diversity of opportunities
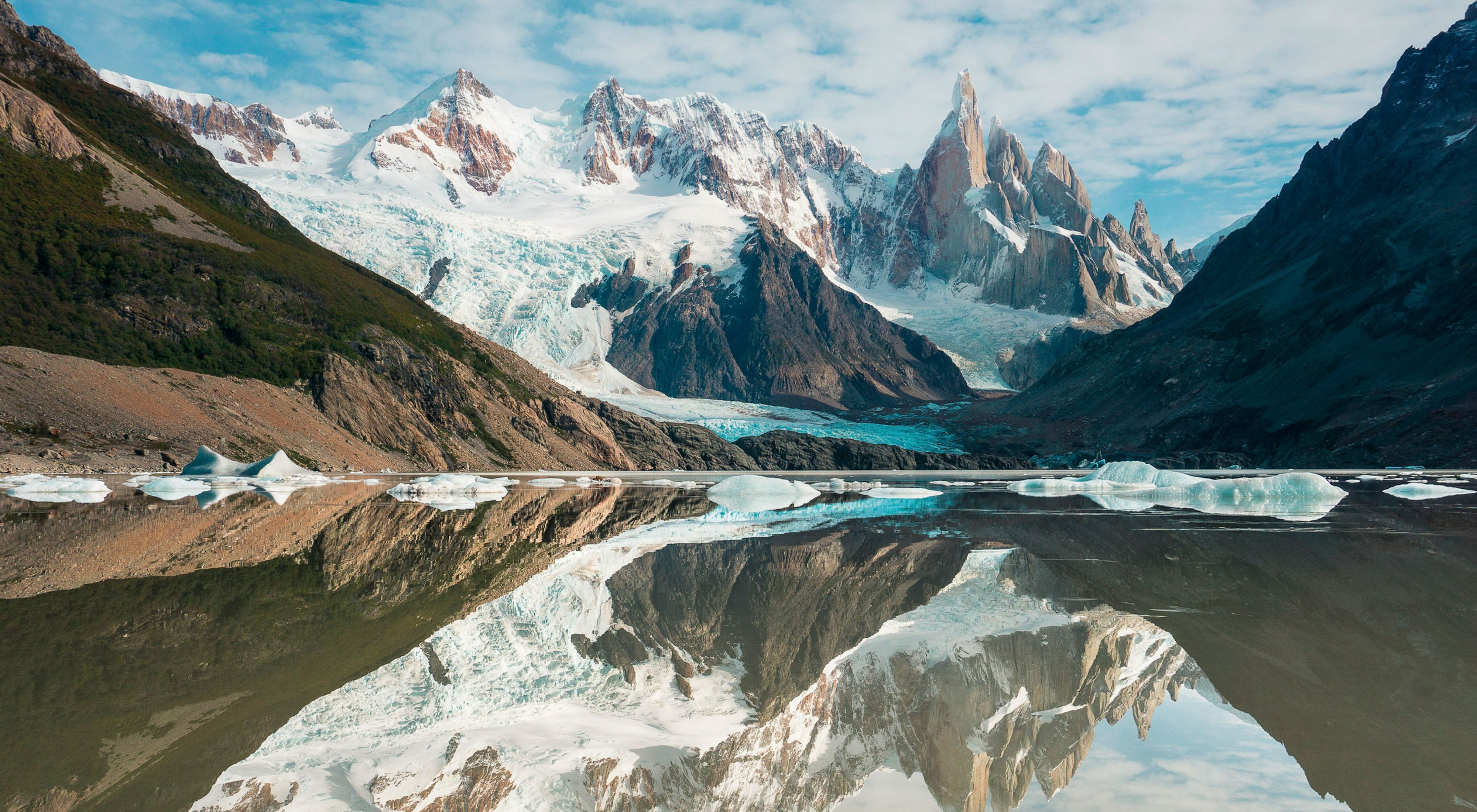
Argentina boasts 18 ecoregions that make up a complex territory, including a subtropical zone, the Antarctic, high mountains, and some of the deepest parts of the Atlantic Ocean.
According to the National Biodiversity Strategy, Argentina is home to over a thousand bird species and hundreds of reptiles, mammals, and amphibians. Unfortunately, 25% of them are under the threat of extinction, according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
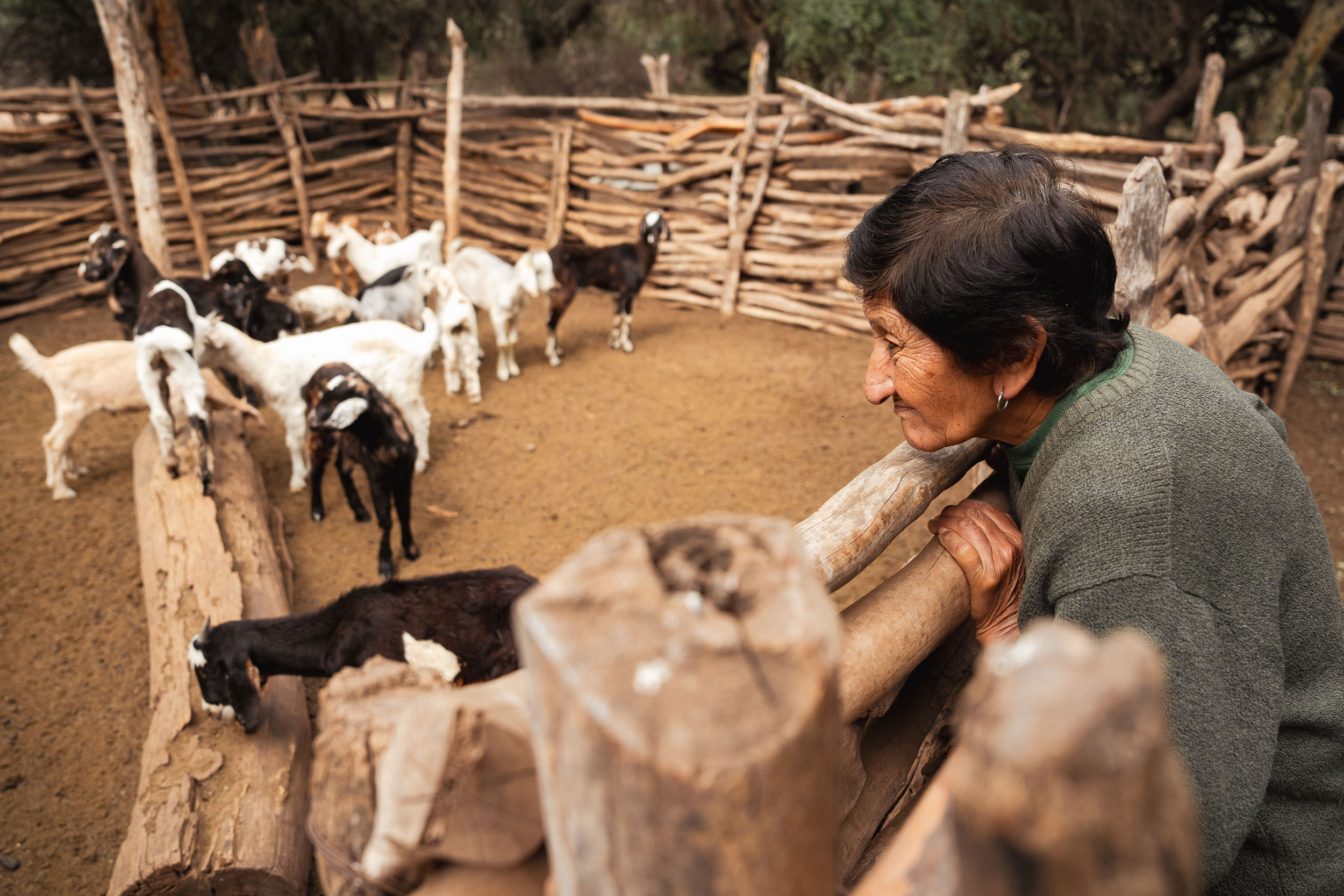
Like many countries in the region, Argentina faces significant challenges related to the constant expansion of agriculture and livestock farming. The growing global demand for food means that cultivated areas continue to increase. Furthermore, deforestation and land-use change have become significant environmental challenges; thousands of Argentinians across the country suffer from droughts and floods annually.
Solutions require systemic thinking, focusing on sustainable models to ensure regeneration and, thus, a successful long-term transition for Argentina, the region, and the world.
TNC works with a collaborative and systemic approach, connecting people with nature through science, smart networks, and shared learning. Involving producers in efforts to maintain the natural foundation of productive lands demonstrates that nature and development can not only coexist but also drive the conservation of forests, grasslands, wetlands, and other ecosystems across the productive landscape, generating positive (scalable and sustainable over time) impacts on the economic, environmental, and social levels.
We can all be agents of change. Being part of this transition is shaping it together. The differential value lies in thinking about complete systems with common objectives.
Strategy and 2030 goals
Since 2008, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) Argentina has been driving initiatives that combine various nature-based solutions to enhance production through innovation (and the implementation of technologies). The efforts have been on generating knowledge and scaling up existing experiences to help promote agricultural sustainability in Argentina. To achieve this, we work with three strategies: (i) Freshwater, (ii) Functional landscapes, and (iii) Forests and carbon.
-

Freshwater
Preserving our freshwater systems, which serve as crucial links between nature and people, ensuring the security and supply of water, both in terms of quality and quantity.
-
Functional landscapes
Promoting healthy agricultural systems that benefit both nature and people, which are climate-resilient, enhance biodiversity, ecosystem conditions in functional landscapes, and social well-being.
-
Forests and carbon
Preserving strategic natural environments and promoting land conservation through a range of strategies, from traditional protection methods to other measures that combine various land uses.

Places We Protect
Where do we work? Explore our Iconic Places
Discover the uniqueness of the iconic places where TNC Argentina, in collaboration with key individuals and organizations in the region, is protecting nature and fostering the pursuit of comprehensive solutions.
We Can’t Save Nature Without You
Sign up to receive regular updates from The Nature Conservancy.








